In Power Automate, “work queues” are a mechanism by which you can organize and distribute tasks or work items to users or teams within an automated workflow. They are useful in situations where you need to manage processes that involve multiple users or require a specific order of execution.
Think of a “work queue” as a traffic intersection during rush hour. Each “item” in the queue represents a vehicle waiting to cross the intersection. The ones who arrived first or have emergency vehicles (priority) get to proceed first.
The “work queue orchestrator” is like the traffic controller. They ensure a smooth flow of traffic and prevent congestion by balancing the workload between the machines.
Vehicles, or queue items, navigate the intersection efficiently when they are managed well, resulting in a faster and more streamlined traffic flow.
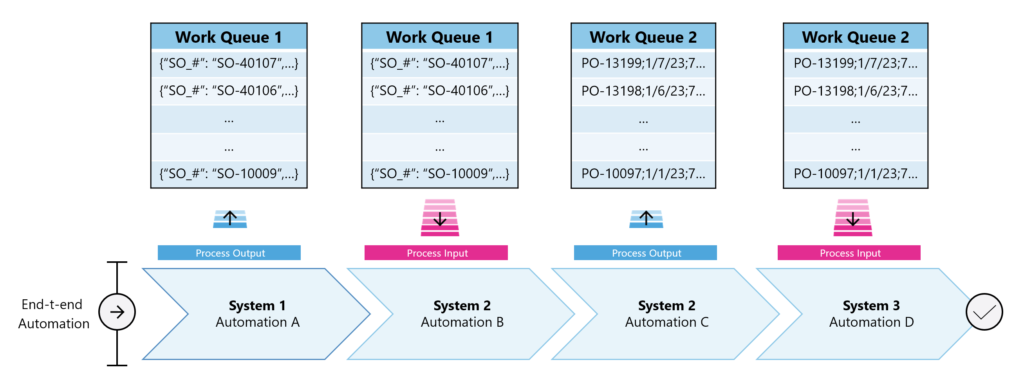
The following illustration shows and end-to-end process that uses work queues to communicate prioritized work between process steps and automations:
- Premium Power Automate license;
- Environment maker role (or other roles that include access to work queue tables).
Example of a typical work queue use case
In a large e-commerce company, there is a high volume of orders that need to be processed daily as part of the supply chain process. To ensure timely processing and adherence to strict service level agreements (SLAs), work queues are utilized.
Here’s how it works:
- Work queue setup: A centrally managed and monitored work queue is created, specifically designed for order processing. It includes relevant details such as order ID, customer information, and order contents.
- Transaction submission: As orders come in, they are pushed into the work queue automatically. Each order is treated as a transaction and becomes an item in the queue.
- Concurrent processing: To speed up the processing, a dedicated machine group consisting of 20 machines is allocated for transaction processing. The work queue orchestrator distributes the transactions among these machines, allowing for concurrent processing.
- SLA compliance: There is a strict deadline for order processing, which is set at 11 PM. The automation is designed to complete the transactions within the SLA. However, in some cases, due to various factors like system issues or complexity, certain transactions may exceed the SLA.
- Manual intervention: When a transaction cannot be processed within the SLA, an alert is triggered, and the responsible users or team are notified. They are responsible for manually addressing the pending transaction to ensure it gets processed on time.
How to get started?
(Source: Microsoft)
Where can you find it?
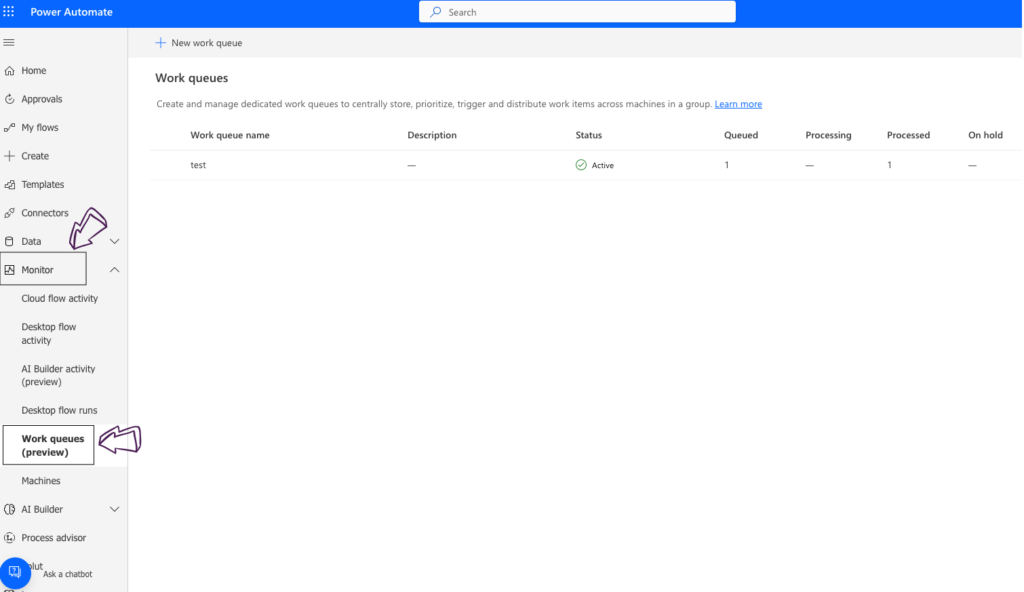
You can find the “Work queues” in Power Automate Cloud – Monitor – Work queues. From there, you have the option to utilize Dataverse actions for adding or processing items. These actions include adding a new row, performing a related action, and updating a row.
Conditions of use:
Here are some key aspects of how work queues work in Power Automate:
- Creating a work queue: In Power Automate, you can create a work queue using an application such as Power Apps or Power Automate Desktop. You can define the relevant fields and properties for the tasks in the queue, such as priority, status, deadline, etc.
- Adding tasks to the queue: You can add tasks or work items to the queue in several ways. These can be added manually by users or can be generated automatically within automated workflows. For example, you can use actions such as “Create a work item” or “Add to queue” to add work items to the queue.
- Assign tasks: Once work items are in the queue, you can assign them to users or teams responsible for execution. This can be done manually or via automated logic. For example, you can use conditions and filters to direct tasks to the right users based on skills, availability or other relevant criteria.
- Task status monitoring: Work queues make it easy to monitor task status. You can track the workflow of a task, including current status, action history and relevant information. You can also set up notifications for users or teams when new tasks become available or when deadlines are approaching.
- Task execution and management: Users can retrieve tasks assigned to them from the queue and work on them. After completing a task, the user can update its status in the queue, which allows monitoring and managing the work process.
With work queues, you can efficiently organise and manage complex tasks or work processes, ensuring that they are distributed and executed in an orderly and coordinated manner.
